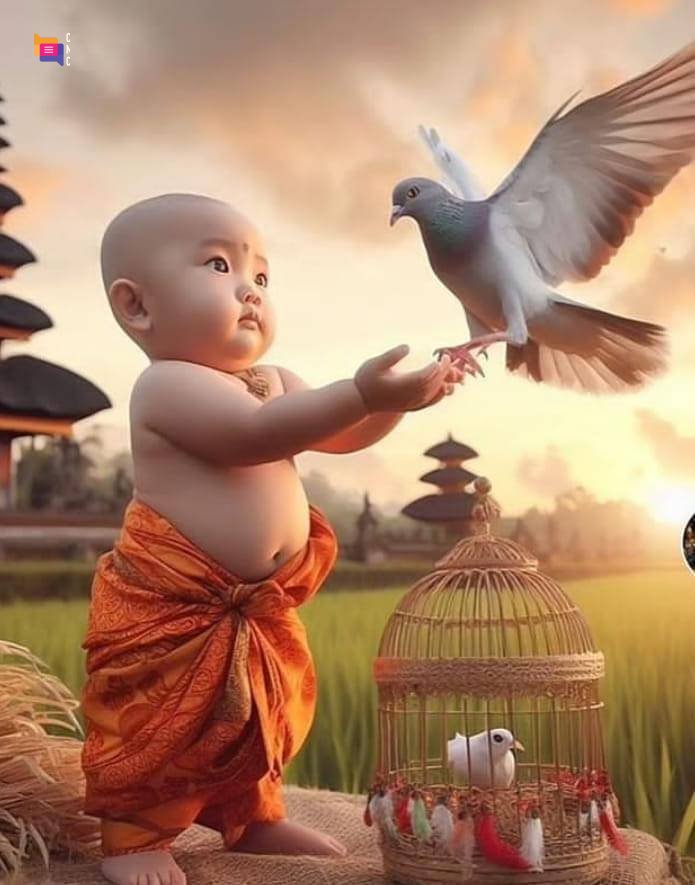
Melhor site de namoro para qualquer idade
Join Quickdate, where you could meet anyone, anywhere! It\'s a complete fun to find a perfect match for you and continue to hook up.
Como funciona
Tornamos mais fácil para você se divertir enquanto usa nossa plataforma Quickdate.
Criar uma conta
Registre sua conta com etapas rápidas e fáceis, quando terminar, você obterá um perfil bonito.
Encontrar correspondências
Pesquise e conecte-se com pares perfeitos para você namorar, é fácil e divertido.
Começar a namorar
Interact using our user friendly platform, Initiate conversations in mints. Date your best matches.
Histórias de sucesso
Encontre sua melhor combinação
Com base na sua localização, encontramos correspondências melhores e adequadas para você.
Totalmente seguro e criptografado
Sua conta está segura no Quickdate. Nunca compartilhamos seus dados com terceiros.
100% de privacidade de dados
Você tem controle total sobre suas informações pessoais que você compartilha.
Por que o Quickdate é a melhor plataforma?
Quickdate, onde você pode conhecer qualquer pessoa digitalmente! É uma diversão completa encontrar uma combinação perfeita para você e continuar a ligar. Mensagens em tempo real e muitos recursos que mantêm você conectado com seu amor 24x365 dias.
Links Rápidos
Sempre atualizado com nossas últimas ofertas e descontos!
direito autoral © 2026 Qimley. Todos os direitos reservados.